Electrochemistry is the branch of chemistry that deals with the relationship between electrical energy and chemical reactions. This field of study has numerous practical applications in our daily lives, ranging from the batteries that power our electronic devices to the industrial production of essential chemicals.
At its core, electrochemistry involves the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy, or vice versa. This process occurs through the transfer of electrons between different substances, often involving ions and electrodes. An electrode is a conductive material that facilitates the transfer of electrons, while an electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity when dissolved in a polar solvent, such as water.
One of the fundamental concepts in electrochemistry is the electrochemical cell. An electrochemical cell consists of two electrodes immersed in an electrolyte solution. When a chemical reaction occurs between the electrodes, it generates an electric potential difference, or voltage, between them. This voltage can be harnessed to perform electrical work, such as powering a device.
There are two main types of electrochemical cells: galvanic cells and electrolytic cells. A galvanic cell, also known as a voltaic cell, is a type of electrochemical cell that generates an electric current through a spontaneous redox reaction. This type of cell is commonly used in batteries, where chemical energy is converted into electrical energy.
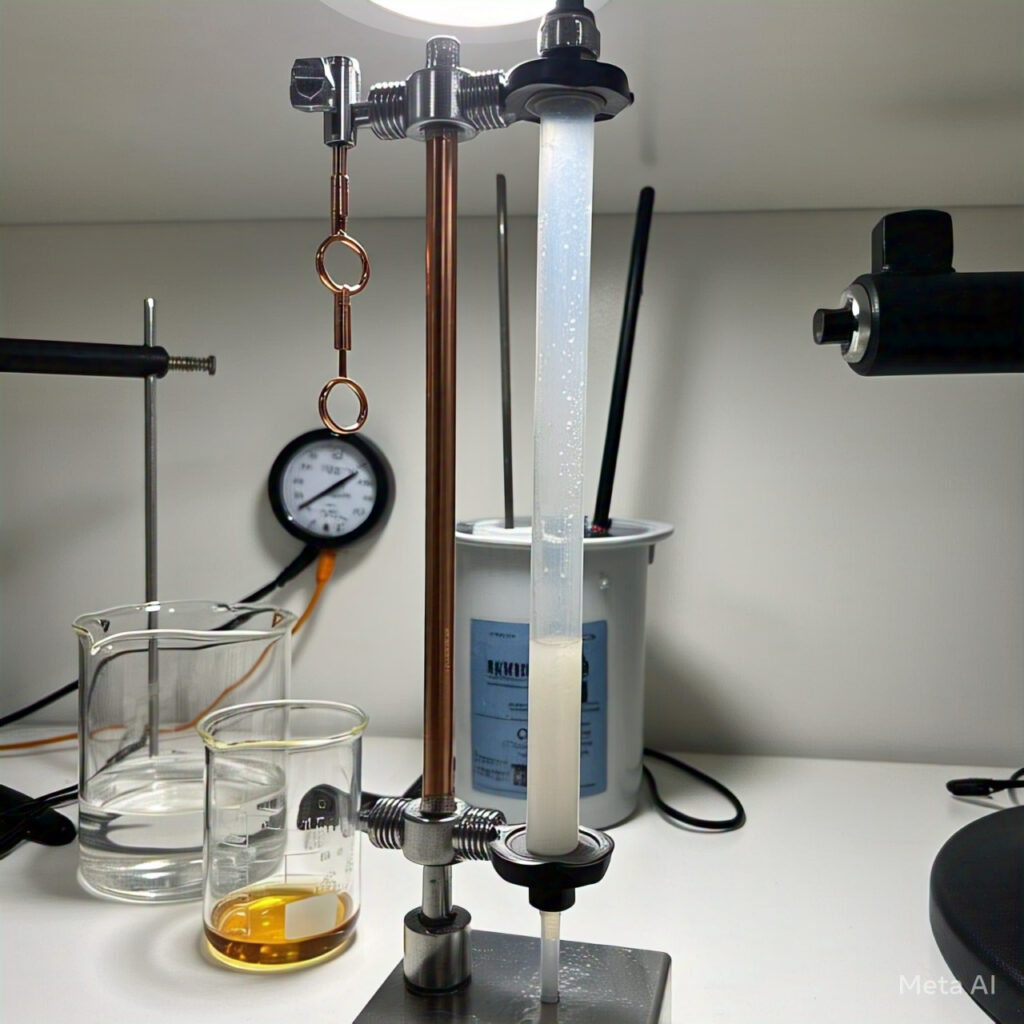

On the other hand, an electrolytic cell is a type of electrochemical cell that uses an external source of electrical energy to drive a non-spontaneous redox reaction. This type of cell is commonly used in electroplating, where a thin layer of a material is deposited onto the surface of another material using an electric current.
Electrochemistry has numerous practical applications in various industries. For example, in the production of metals like aluminum and copper, electrolysis is used to extract the metal from its ore. Similarly, in the manufacturing of chemicals like chlorine and sodium hydroxide, electrolysis is used to produce these essential chemicals.
In addition, electrochemistry plays a crucial role in the development of sustainable energy solutions. For instance, fuel cells, which convert chemical energy into electrical energy, have the potential to replace traditional fossil fuels as a cleaner and more efficient source of energy.
In conclusion, electrochemistry is a vital field of study that has numerous practical applications in our daily lives. From the batteries that power our electronic devices to the industrial production of essential chemicals, electrochemistry plays a crucial role in many industries. As we continue to develop new technologies and seek sustainable energy solutions, the importance of electrochemistry will only continue to grow.