In our day to day life, we come across a number of alkyl halides like chloroform, freon, etc. In this chapter, we will discuss the different types, Isomerism, and the preparation of alkyl halides. After completion of this portion you may complete the reactions of alkyl halides, preparation, and reactions of chlorobenzene and Practice set.
1. TYPES OF HALIDES:
a. Haloalkane or alky halide:
When halogen atom(s) is bonded to an alkyl group, it is called haloalkanes or alkyl halides.
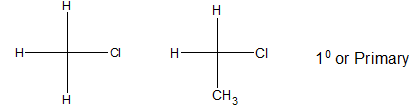
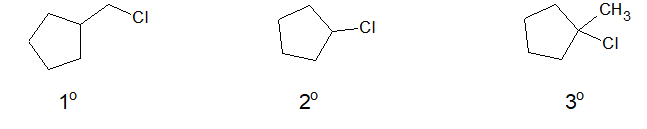
i) Primary alkyl halide:
If 2 directly bonded atoms remain connected with the carbon atom holding halogen, it is said to be 1o or primary alkyl halide.
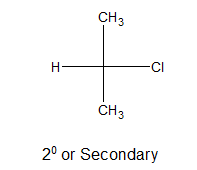
ii) Secondary alkyl halides:
If a single directly bonded atom remain connected with the carbon atom holding halogen, it is said to be 2o or secondary alkyl halide.
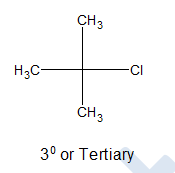
iii) Tertiary alkyl halides:
If their is no directly bonded hydrogen connected with the carbon atom holding halogen, it is said to be 3o or tertiary alkyl halide.
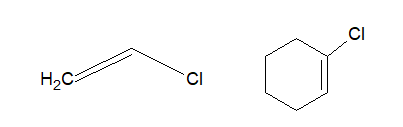
b. Halocycloalkane or cycloalkyl halide:
When cycloalkanes are bonded with halogen, it is called halocycloalkane or cyclyoalkyl halide.
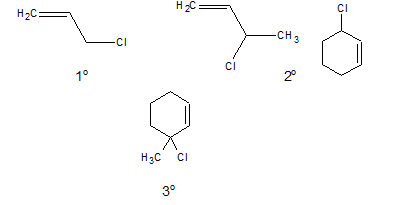
c. Allylic halide:
In allylic halides the halogen atom is linked to a sp3 hybridised carbon atom which is next to a carbon-carbon double bond.
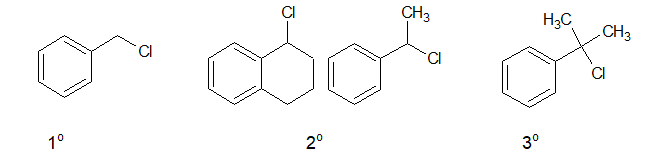
d. Benzylic halide:
In Benzylic halides, the halogen atom is attached to a sp3 hybridised carbon atom which is next to an aromatic ring.
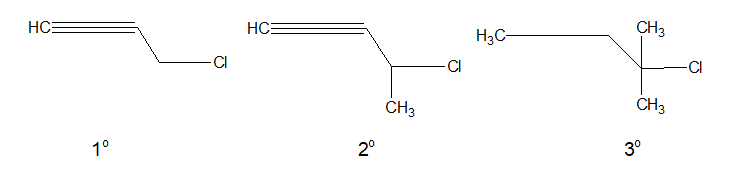
e. Propargyl halide:
In Propargyl halides, the halogen atom is linked to a sp3 hybridised carbon atom which is next to a carbon-carbon triple bond.
f. Vinyl halide:
In Vinyl halides, the halogen atom is attached to one of the carbon atoms of the carbon-carbon double bond.
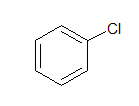
g. Aryl halide:
In Aryl halides, the halogen atom is directly attached to aromatic ring.
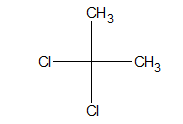
h. Gem dihalide:
When halogen atoms are attached to the same atom, it is said to be a gem halide.
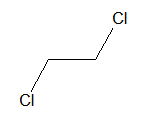
i. Vicinal dihalide:
When two halogen atoms are attached on adjacent carbon atoms it is called vicinal halide.
2. ISOMERISM IN ALKYL HALIDES
a. Chain isomerism:
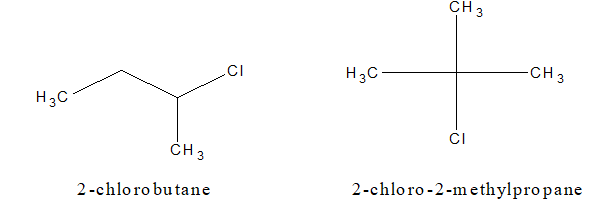
b. Position isomerism:
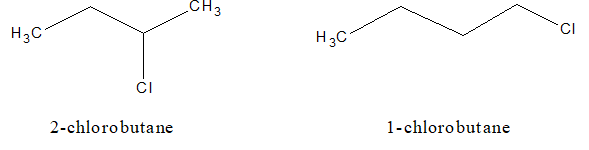
c. Optical isomerism:
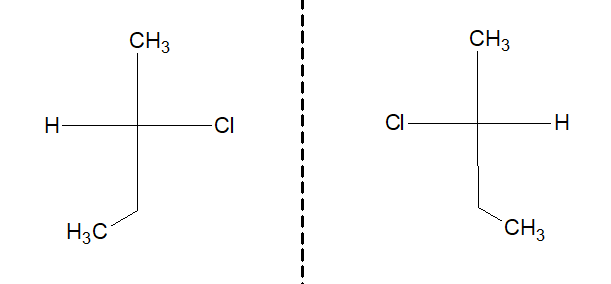
Nature of C-X bond
Due to the electronegativity difference between carbon and halogen, the c-X bond is polar in nature.
- Bond length: C-F<C-Cl<C-Br<C-I ( increases with the size of the halogen)
- Bond energy: C-F>C-Cl>C-Br>C-I (Decreases with the size of the halogen)
- Dipole moment: C-Cl>C-F>C-Br>C-I (Decreases with the electron affinity of the halogen)
3. Preparation of Haloalkanes
a. From Alcohol:
1)When alcohol is treated with HBr or HI or HCl/Anh ZnCl2 the OH group gets substituted by the halogen atom.
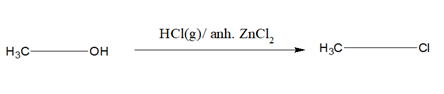
i)HCl requires anh. ZnCl2 as a catalyst. A mixture of Conc.HCl and anh.ZnCl2 is known as Lucas reagent. This is called Groove’s process. For 30 alcohol, anh.ZnCl2 is not required.
ii)HCl<HBr<HI, reactivity order.
iii)1o<2o<3o, the reactivity for a specific HX.
iv)To prepare bromoalkane, NaBr/ H2SO4 is used.To prepare iodoalkane, KI/ H3PO4 is used.
2) When alcohol is reacted with PCl5 or PCl3 the OH group gets substituted by the chlorine atom.

i)PBr5 and PI5 are unstable compounds.
ii)As PBr3 and PI3 are unstable compounds, PBr3 and PI3 are produced insitu by the reaction of P4 and Br2 or I2.
3. When alcohol is reacted with SOCl2 / Pyridine, the OH group gets substituted by the chlorine atom.
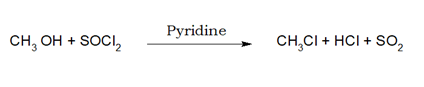
i)When thionyl chloride is used, HCl and SO2 are produced as gaseous product , and can be easily separated.
ii)When pyridine is used, HCl reacts with pyridine.
iii)This process is called Darzens process. iv)RBr and RI cannot be prepared by this method as SOBr2 is less stable and SOI2 does not exist.
b.From Alkanes:
1.Chlorination and Bromination:
Alkanes when reacted with chlorine or bromine in the presence of diffused sunlight (Cl2/hν or Br2/hν), chloroalkane or bromoalkane is formed.
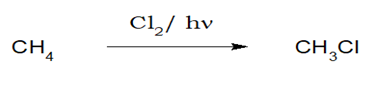
i)Benzylic ≈ allylic > tertiary > sec> pri > vinylic ≈ aryl . The reactivity of different types of hydrogens.
ii)Halogentaion of alkane follows free radical mechanism.
iii)F2>Cl2>Br2>I2 is the order of halogenations for a particular alkane.
iv)Direct fluorination is explosive. v)For halogenations on an aliphatic chain with more than 2 carbon, halogen always tries to avoid the peripheral carbons.
2.Fluorination:
Preparation of fluoride from bromide and chloride by using AsF3, SbF3, CoF2, AgF, Hg2F2 etc is called Swarts Reaction.
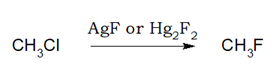
3.Iodination:
Iodination of alkyl chloride or bromide by NaI in acetone or methanol medium is called Finkelstein Reaction.
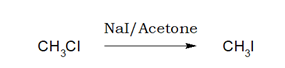
Iodination of an alkane is reversible in nature. Hence to make it irreversible HIO3 or HNO3 or HgO is used. CH4 + I2 →CH3I + HI
5HI + HIO3 → 3I2 + 3H2O
c. From Alkenes:
Alkenes when reacted with HCl or HBr or HI, respective haloalkane is produced.
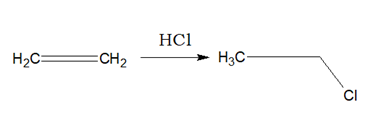
i)Addition of HX will follow Markownikoff’s Rule.
ii)Addition of HBr in presence of organic peroxide is called peroxide effect or Kharasch effect where anti Markownikoff’s product is formed.
iii)The addition of HBr is a double step reaction, which is exothermic. But with HCl the second step is endothermic. With HI the first step is endothermic. iv)The peroxide effect will follow radical mechanism.
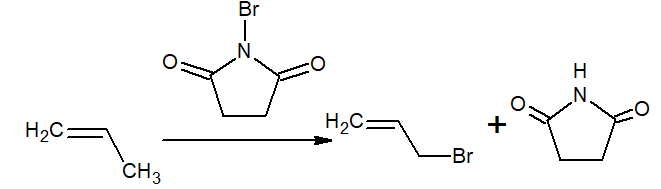
iv)Allylic bromination or chlorination is carried out by NBS/hν (for bromination) and SO2Cl2/hν/200oC/OPO ( for Chlorination)
d. From Silver salt of carboxylic acid:
Silver carboxylates when treated with Br2 or Cl2 in presence of CCl4 produce alkyl bromide or chloride with a carbon less.
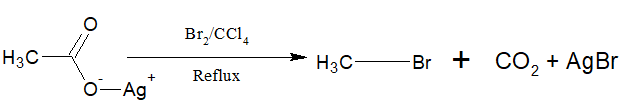
i)The reaction is called Hunsdiecker reaction.
ii) Aryl bromide can also be prepared by this method.
iii)The yield is 10>20>30
iv)Chlorine gives a poor yield
v)It is believed to follow free radical mechanism.
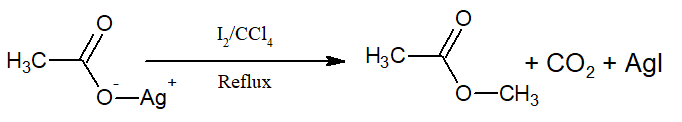
vi)Ehen the same reaction is carried with I2, ester is produced. This reaction is called Birnbaum-Simonini reaction.