1.Matter:
Matter is a physical substance which possess mass, occupies space, and can be perceived by any one or more sense organs.
2. Kinetic Theory of Matter:
The kinetic Theory of matter is a concept that basically states that matter is made up of atoms and molecules which remain in constant motion due to kinetic energy possessed by them.
Kinetic theory is useful in explaining the different physical states of matter, change in state, effects of heat and pressure on matter and transfer of heat through matter.
Postulated of the Kinetic Theory of Matter
- All matter is made up of tiny particles called atoms, that joined together to form molecules.
- These particles are in constant motion, in all possible direction, with all possible velocities, due to the presence of kinetic energy.This kinetic energy increases with temperature.
- Several kinds of forces of attraction exist between the molecules. These forces are called inter molecular forces of attraction. This force of attraction decreases with the increase in the energy of the molecules.
- The molecules collide with themselves and also with the wall of the container.
- Every particles has empty space between each other called inter molecular space. Greater the inter molecular force of attraction, lesser the inter molecular space between the molecules.
3. Physical states of Matter
Solid , Liquid and Gases are the three main physical states of matter. Along with these three Plasma, Bose-Einstein Condensates are also studied.
| Property/Feature | Solid | Liquid | Gas |
| Arrangement of particles | Closely packed | Moderately close to each other | Far apart from each other |
| Total energy content | Low | High | Highest |
| Movement of particles | Vibrate about a fixed position | Slide around each other | Move rapidly in any direction |
| Inter molecular attraction | Greatest | High | Least |
| Inter molecular space | Minimum | Moderate | Maximum |
| Consistency | Rigid, have fixed shape | Can flow and take the shape of the container | Can flow and completely fill the container |
| Compressibility | Cannot be compressed | Undergoes minimum compressibility under high pressure. | Can be easily compressed |
Explanation with respect to the kinetic theory of matter
- Solid:
In solid-state, the particles are closely packed with each other. The potential and kinetic energy possessed by the particles are very low. The particles can only vibrate about a fixed position. As the particles cannot move from place to place, they are rigid and have fixed shapes.
As their is no inter molecular space between the particles, they cannot be compressed.
When solids are heated, heat energy gets converted partially to potential energy and the remaining to kinetic energy, thus vibration of particles gets faster. The intermolecular attraction decreases, which in turn increases intermolecular space. Thus solids expand on heating.
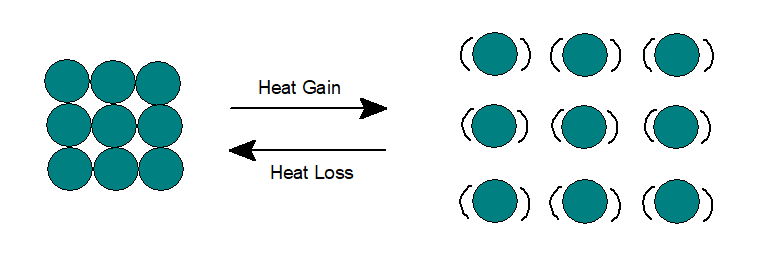
2. Liquid :
In liquid state, The potential and kinetic energy of the particles are higher than solid. Particles have random arrangement with inter molecular space.
Particles move around each other and thus can flow and take the shape of the container. As very little space are available for the particles to move, thus liquids possess minimum compressibility under high pressure.
Like solids, when liquids are heated, heat energy gets converted partially to potential energy and the remaining to kinetic energy, thus vibration of particles gets faster. The inter molecular attraction decreases, which in turn increases inter molecular space. Thus liquids expand on heating.
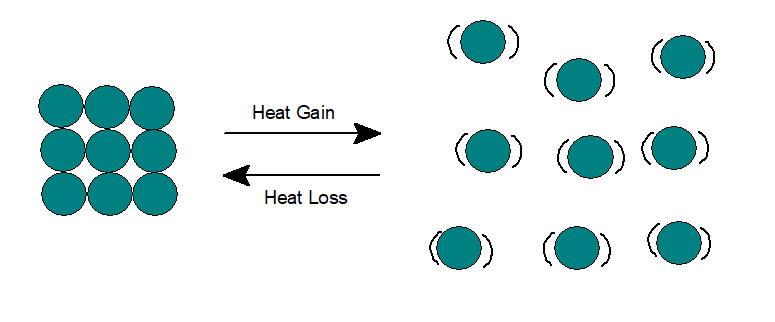
3. Gas:
In gases, both potential and kinetic energy are higher than liquids. The gas molecules can move rapidly in any direction and thus can flow to completely fill the container. Particles remain far from each other and thus can be easily compressed to a large extent.
When heated, the heat energy gets partially converted to potential energy and the remaining to kinetic energy. Intermolecular attraction decreases even further, thus increasing the intermolecular space to a large extent. If the gas remains in a closed container, the pressure will increase as more particles will collide with the wall of the container.
Liquid and gases are called fluid as they can flow.
4. Change of state of Matter:
Change of state of matter is a phenomenon of transition of matter from one state to another.
When a solid is heated at a constant pressure, it gradually changes to liquid and then to a gas.
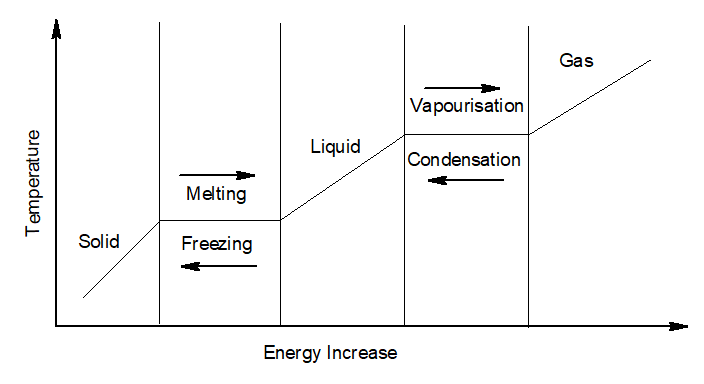
- Melting or fusion– The process of conversion of a solid to liquid on the application of heat at a constant temperature is called melting or fusion.
- Melting point– The temperature at which a solid change to liquid on applying heat is called the melting point of that solid.
- Boiling– The process of conversion of a liquid to gas on the application of heat at a constant temperature is called boiling.
- Boiling point– The temperature at which a liquid change to gas on applying heat is called the melting point of that solid.
- Condensation -The process of conversion of a gas to its liquid state by loss of heat at a constant temperature is called condensation.
- Condensation point– The temperature at which a gas changes to liquid state by losing heat is called the condensation point.
- Freezing– The process of conversion of a liquid to its gaseous state by loss of heat at a constant temperature is called freezing.
- Freezing point-The temperature at which a liquid changes to the gaseous state by losing heat is called the freezing point.
- Sublimation– The process of conversion of a solid directly to the gaseous state on applying heat is called sublimation. Camphor, naphthalene, dry ice, iodine, benzoic acid, etc show sublimation.
- Deposition– The process of conversion of gas directly to the solid-state by losing heat is called deposition.
- Evaporation– Evaporation is the conversion of a liquid to its gaseous state only on the surface. It happens all the time, at all temperatures and pressure. It causes a cooling effect.
5. Plasma
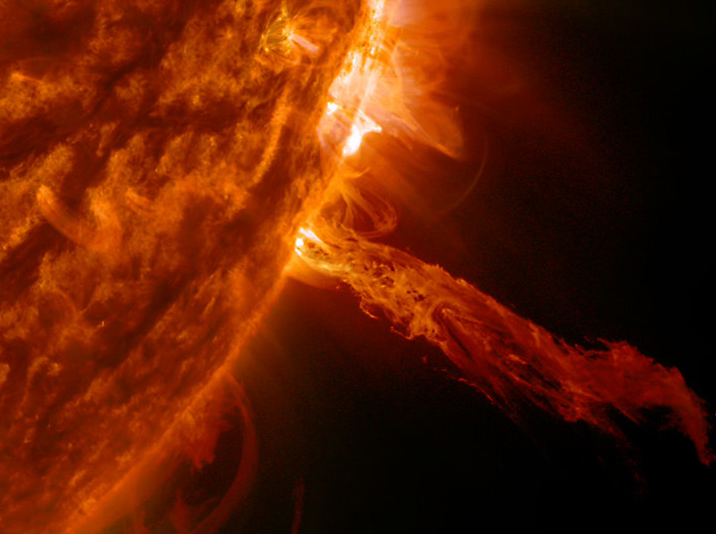
Plasma is basically a highly energized gas. Physically it is gaseous with super excited positively and negatively charged particles instead of molecules or atoms.
Plasma state can be seen near the sun. The aurora is caused due to plasma. Plasma TV and neon lights are the uses of plasma.
Conversion of gases to plasma is called ionization. The reverse process is called recombination.

6. BEC
Bose-einstein Condensate is another state of matter that exist at a very low temperature (-273.15 °C). Particles shows no movement and cling together.
7. Law of conservation of mass:
The Law of conservation of mass states that the mass of the reactants and the mass of the products in a chemical reaction are equal.
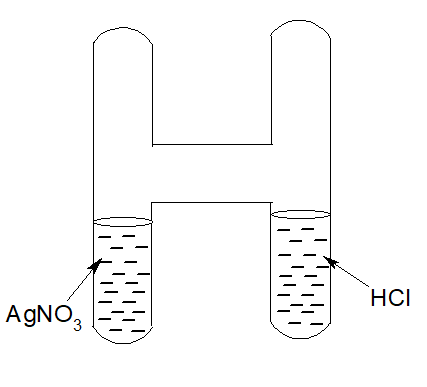
Silver nitrate solution is taken in one limb of an H-shaped and hydrochloric acid in another limb and weighed. After that, the solutions are mixed. A curdy white ppt of Silver chloride is produced. It is weighed again. It is seen,
Wt of Silver nitrate + Wt of Hydrochloric acid= Wt of Silver chloride + Wt of nitric acid
AgNO3 + HCl → AgCl + HNO3














